Plants are autotrophic(auto- self * trophic- feeding)
Photosynthesis (photo-light * synthesis- build up)
- Photosynthesis is the manufacturing of organic compounds primarily carbohydrates (eg glucose) by green plants from carbon dioxide and water using sunlight
- it occurs in the green plants
Word Equation
- carbon dioxide + water ⇨ glucose + oxygen
- glucose is used during respiration and can be stored as starch(insoluble)
- oxygen is used during respiration
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
- temperature
- carbon dioxide
- light
- water
- surface area of leaves
- chloroplast
Limiting factors
process controlled by many factors have its rate determined by a factor which is in shortest supply
- light intensity
- carbon dioxide concentration
- temperature
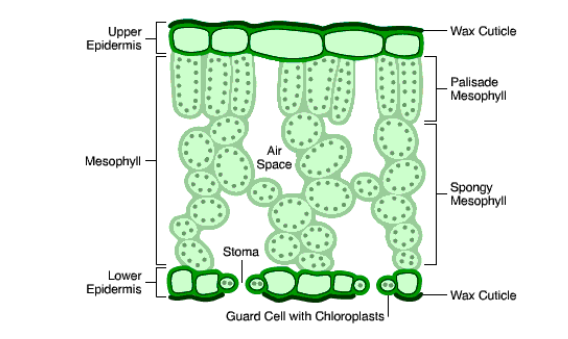
The internal structure of a Dicotyledonous leaf
cotyledon is a food storing leaf
MICROSCOPIC CROSS SECTION THROUGH A DICOT LEAF
Parts and Functions
- Cuticle
- forms a hard surface on top of the leaf to prevent water loss
- Upper epidermis
- forms a single layer of cells (forms the upper part of the leaf).
- Palisade mesophyll
- cells have plenty of chloroplasts- where most photosynthesis takes place.
- Spongy mesophyll
- cells in this zone are not closely packed together to allow easy movement of gases.
- Stomata
- these are openings mostly found on the lower part of the leaf on land plants that allow gaseous exchange. These are bound in the lower epidermis
- Guard cells
- they control the opening and closure of the stomata.
- Loer epidermis
- forms the lower part of the leaf
- Vascular bundle
- it is made up of xylem vessels and phloem tubes
- Xylem vessels
- transport water and dissolved minerals
- Phloem tubes
- transport the manufactured food
- Chloroplasts
- the green pigments inn a leaf that give leaves their color
How structure of a leaf is adapted to its functions
- Cuticle
- waxy
- transparent
- water impermeable so prevent water loss
- allows light to pass through
- Upper epidermis
-
- transparent
- no intercellular spaces
- it prevents the water loss
- Palisade mesophyll
-
- just below the upper epidermis
- cell longitudinally placed
- closely packed chloroplasts to absorbs much sunlight as possible during photosynthesis
- large vacuole pushes the chloroplasts toward the outer region so they can absorb more light
- Spongy mesophyll
-
- it has intercellular spaces
- the walls are moist
- help in gaseous exchange i.e diffusion of gases
- Guard cells
-
- they regulate the opening and closure of stomata
- help in gaseous exchange
- prevent excessive water loss
- Vascular bundles
-
- transport of water & dissolved minerals and food
You absolutely know how to keep your readers interest with your witty thoughts on that topic. I was looking for additional resources, and I am glad I came across your site. Feel free to check my website QH9 about Airport Transfer.