Definition
- is the maintenance of a constant internal environment(temperature), water and glucose concentration
- Negative feedback is a main process involved
- Negative feedback is a series of events in response to a deviation from a normal condition to bring the change back to normal
The importance of Homeostasis
- enables organisms to occupy diverse places
- stay active in all seasons
- continue metabolic at an optimum level
Examples of homeostasis
- thermoregulation
- blood glucose regulation
- osmoregulation
The skin and temperature control
Functions of the skin
- prevent entry of pathogen into the body
- prevent the loss of body fluids
- maintains body temperature
- excretion of excess water, salts, urea ..
Structure of the skin
- it is made up of two layers
- Epidermis-too thin layer
- Dermis -thicker layer below the epidermis
Epidermis
- It has three layers
- Cornified layer made up of flat, dead cells that prevent water loss and entry of pathogens
- Granular layer made of living cells that will replace cornified layer
- Malpigian layer- consists of actively cells which contains melanin that gives colour to the skin
Dermis
- consists of blood vessels, nerve endings, sweat glands, hairs and fatty/dipose tissue
- Dipose tissue creates an insulating layer which reduces heat loss.
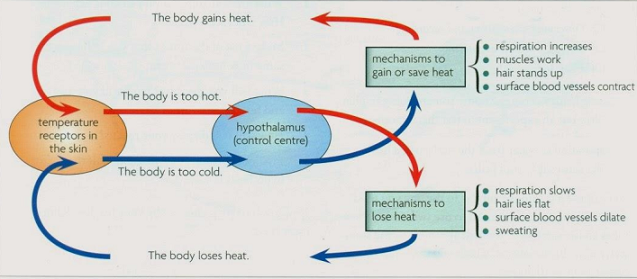
- Receptors(nerve endings) detect any significant temperature changes in the brain (hypothalamus) and response is given to correct the change.
Hypothalamus act as a thermostat - Hairs provide a layer of insulating air over the skin surface.
The hairs erect due to the constriction of microscopic muscle fibres- this causes ‘goose bumbs’ when a person is cold - The sweat glands secrete sweat which during evaporation has cooling effect.
- A dense network of blood vessels brings heat within the body.
- when temperature increases the flow of blood increases in the arterioles as they dilate (vasodilation) and more heat is lost by radiation from the body
- when temperature drops the arterioles contract (vasoconstriction) and temp is controlled since less heat is radiated
Temperature regulation
Shivering
it occurs due to rapid muscle movement which generates heat enrgy which increases the body temperature