Skeletal System
- it consist of three main types of tissues;
- muscles
- bones
- cartilage
Functions of the skeletal system
- protection
- Support
- Muscle attachment
- movement
- storage of calcium
- blood cells formation
Main types of skeletal system;
- exoskeleton in insects
- its functions include support, attachment of muscle for movement, protection and prevent water loss
- endoskeletons in vertebrates(eg humans)
- its functions include support, protection and movement
Skeleton of Humans
- it is divided into three parts:
- Axial skeleton-skull, back bone and ribs
- Appendicular skeleton-limbs
- Girdles-hip and shoulder girder
Bones
Pectoral girdle- shoulder
CONSIST OF;
- Shoulder
- a triangular, flat bone witha shallow cavity on narrower end. It joins the arm tto the axial skeleton.
- The collar bone
- it prevents the shoulder from bending inward.
- Arm – upper and lower arm
- Ulna and radius
- ulna is longer and thicker than radius
- has cavity where part of humorous fitted to make a hinge joint
- ulna has an extended bone
- Humorous
- A long bone with a rounded head-epiphysis and a long central shaft-endophysis
- Shallow cavity
- lose attachment oof the shoulder bone with the back side of ribs
Joints
Is a connection between two or more joints. They provide articulation between bones making movement possible.
Types of joints
Gliding joint
- e.g joints which occur between the vertebrate wrists and ankles
- the ends of the bones that make the joint are covered with cartilage
- they are held together by tough ligaments
Synovial joint
- it is enclosed by fibrous capsule lined by synovial membrane which secretes synovial fluid into the synovial cavity
- the synovial fluid lubricates the joint
- they include hinge and ball and socket joints
Hinge joint
- eg knee joint
- it allows movement in one plane, ball and socket joint
- eg hip joint;
- it allows rotation in all directions
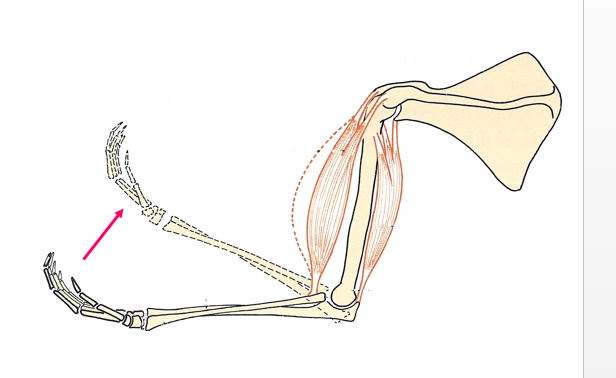
ELBOW
Role of muscles in movement of human arm
Muscles that bring about movement are antagonistic i.e when one set contracts the other relaxes
- Movement of the hinge joint of an arm
- moving arm upwards(biceps flexor) muscle contract whilst triceps muscle relax
- straightening the arm, biceps muscle relaxes whilst the triceps(extensor) muscle contract
Antagonistic muscle of human forelimb
- the biceps muscles of the forelimb act as flexors while the triceps muscle act as extensors
- the biceps has its points of origin on the scapula and the point of insertion on the radius
- the triceps has its point of origin on the scapula and humorous and is inserted on the ulna
- when the muscles contract, the limb act as a lever with the pivot at the joint
- contraction of biceps muscles bends the arms while contractions of triceps extend the arm