The Brønsted-Lowry acid-base concept
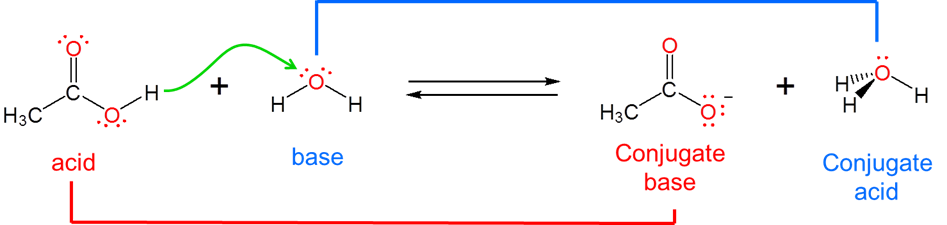
Brønsted acid is a substance that loses an H+ ion by donating it to a base. and Brønsted base is defined as a substance which accepts H+ from an acid when it reacts.
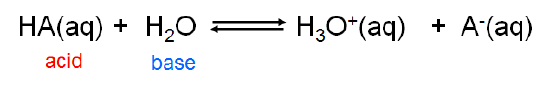
Similarly, Arrhenius bases act as Brønsted bases in accepting a hydrogen ion from the Brønsted acid water:
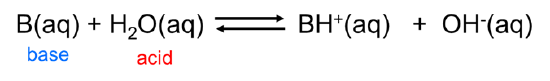
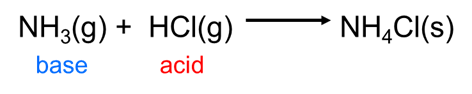
Conjugate Acids and Bases
Brønsted-Lowry system makes it easy to recognize that when an acid loses its hydrogen ion it becomes capable of receiving it back again, thus becoming a base. Consider, for example, the base dissociation of ammonia in water. When ammonia acts as a Brønsted base and receives a hydrogen ion from water, ammonium ion and hydroxide are formed:

The ammonium ion is itself a weak acid that can undergo dissociation:
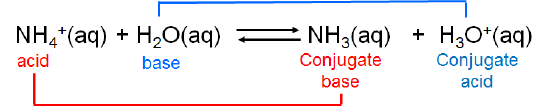
In this case ammonia and ammonium ion are acid-base conjugates.
The strengths of conjugates vary reciprocally with one another, so the stronger the acid the weaker the base and vice versa. For example, in water, acetic acid acts as a weak Brønsted acid:
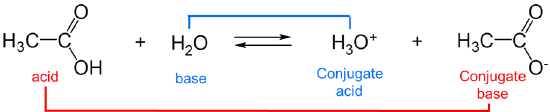
and acetic acid’s conjugate base, acetate, acts as a weak Brønsted base.
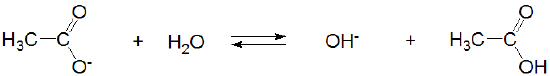
However, in liquid ammonia acetic acid acts as a strong Brønsted acid:

while its conjugate base, acetate, is neutral.
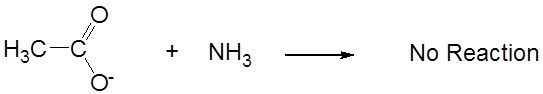
The reciprocal relationship between the strengths of acids and their conjugate bases has several consequences:
- Under conditions when an acid or base acts as a weak acid or base its conjugate acts as weak as well. Conversely, when an acid or base acts as a strong acid or base its conjugate acts as a neutral species.
- When a Brønsted acid and base react with one another, the equilibrium favors formation of the weakest acid-base pair.