Electrostatic charging
- Friction between objects can cause electrons to be transferred from one object to another. When the object gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged. When an object loses electrons it becomes positively charged. Perspex attains positive charge while polythene attains negative charge.

- Rub a polythene rod with a woollen cloth and suspend the charged rod by a cotton thread from a retort stand. Charge a second polythene rod and bring it towards the suspended rod and repulsion occurs i.e. like charges repel. Charge a perspex rod towards the suspended polythene rod and attraction occurs i.e. unlike charges attract.
Gold leaf electroscope

- The gold leaf electroscope is a simple instrument used to detect electric charges
- A gold-leaf electroscope consists of a brass rod, with a brass (metal) cap and a brass plate at the bottom. A thin leaf of gold or aluminium foil is attached to the brass plate. The brass rod is mounted in a glass case, supported by a plug of insulating material
Detecting a charge
- When the gold leaf is close to the brass plate in a collapse state then the brass cap, brass rod, brass plate and the gold leaf are electrically neutral. There is no excess charge.
- When a charged insulator (such as a positively-charged glass rod) is brought near to the brass cap, the free electrons from the brass and gold parts of the electroscope are attracted to the brass cap leaving the brass plate and gold leaf positively charged. This causes the gold leaf to diverge due to the repulsion between like positive charges.

Charging an electroscope
- To charge the electroscope negatively, slide a negatively charged rod on the brass cap of the electroscope so that some electrons from the charged rod can be transferred to the cap causing the gold leaf to deflect or diverge.
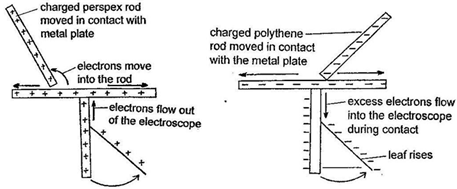
- Charge detection uses only the phenomenon of repulsion between like charges is used
Lightning
Production of lightning
- The thunder clouds are charged by friction between the water molecules in the thundercloud and the air molecules
- As violent movement on the cloud continues, charging also continues i.e. very high voltage build up between the positive and negative charges within the cloud.
- When the charge on the thundercloud is sufficiently large, it can ionise the air which then provides a conducting path for the huge quantity of charge to be discharged to the nearest or sharpest object on the ground

The principle of a lightning conductor
- The lightning conductor provides an alternative steady path for the flow of charge from the top of the building to the earth.
- When a negatively charged thundercloud passes overhead, it acts inductively on the conductor, charging the spikes positively and the earth plate negatively.

- Negative electrons are attracted to the spikes and become discharged.
- The electrons are then passed down the conductor and are dissipated (earthed) to the ground from the copper plate.
- The conductor is placed above the building to collect charges and pass it harmlessly into the earth.
- The conductor is made of thick copper strip to conduct electrons to the ground since copper is a good conductor of electricity.
- The copper strip is attached to a copper plate in the ground to earth excess electrons
Dangers of lightning
- Light voltage causes outbreak of fire
- Flow of current result in electrocution and severe burns
- Heating effect of current cause destruction of buildings
Safety precaution against lightning
- Keep away from metallic objects
- Disconnect roof top aerials
- Do not shelter near or under isolated trees
- Disconnect electrical appliances
- Avoid being in contact with water during a lightning storm i.e. swimming
1 Comment
binance us register
July 25, 2024Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.