Introduction
- Rate of a reaction: change in concentration of reactants or products per unit time
- Activation energy: minimum energy colliding particles must possess for a successful collision to take place
- Catalysis: acceleration of a chemical reaction by catalyst
Effect of Concentration Changes
- Increasing conc. of reactants increases rate of reaction: more particles per unit volume, collision rate between reacting particles increases, ∴∴ rate of successful collision increases, resulting in increased rate of reaction.
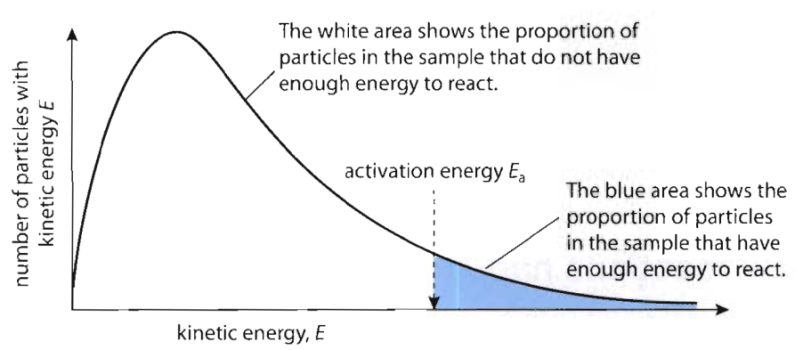
Maxwell-Boltzmann Theory
- Explains effect of temp. & catalyst on rate of reaction
- Based on distribution of energy among reacting molecules under different conditions
Effect of Temperature
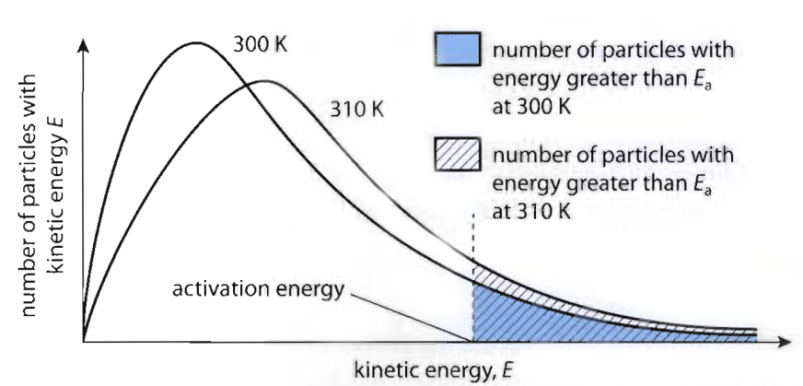
- Number of collisions and chance of success will increase
Effect of Catalyst
- Catalyst: a substance that increases rate of reaction but remains chemically unchanged itself at the end
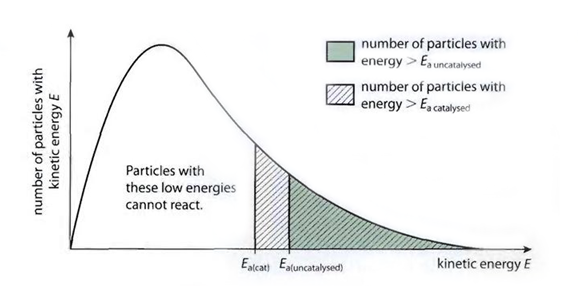
- Does not alter the chemical composition of substances and only lowers the activation energy
- It provides a new route or mechanism to follow for reactants that requires less energy
- Curve unchanged, only activation energy changes
- Homogeneous catalysts: reactant and catalyst are in the same physical state
- Heterogeneous catalysts: reactant and catalyst are in different physical states
- Enzymes: a protein molecule that is a biological catalyst. Most are specific to a substrate & function as lock-key